Egg freezing, or oocyte cryopreservation, is an increasingly popular fertility preservation technique that allows women to store their eggs for future use. As more women prioritise career, personal development, or face health concerns that may affect fertility, egg freezing offers a way to extend the window of opportunity for having biological children. This process has evolved significantly over the years, thanks to advances in medical technology, making it a viable option for many women. In this blog, we’ll explore what egg freezing entails, who might benefit from it, the process itself, and key considerations when making this important decision.
What is Egg Freezing?
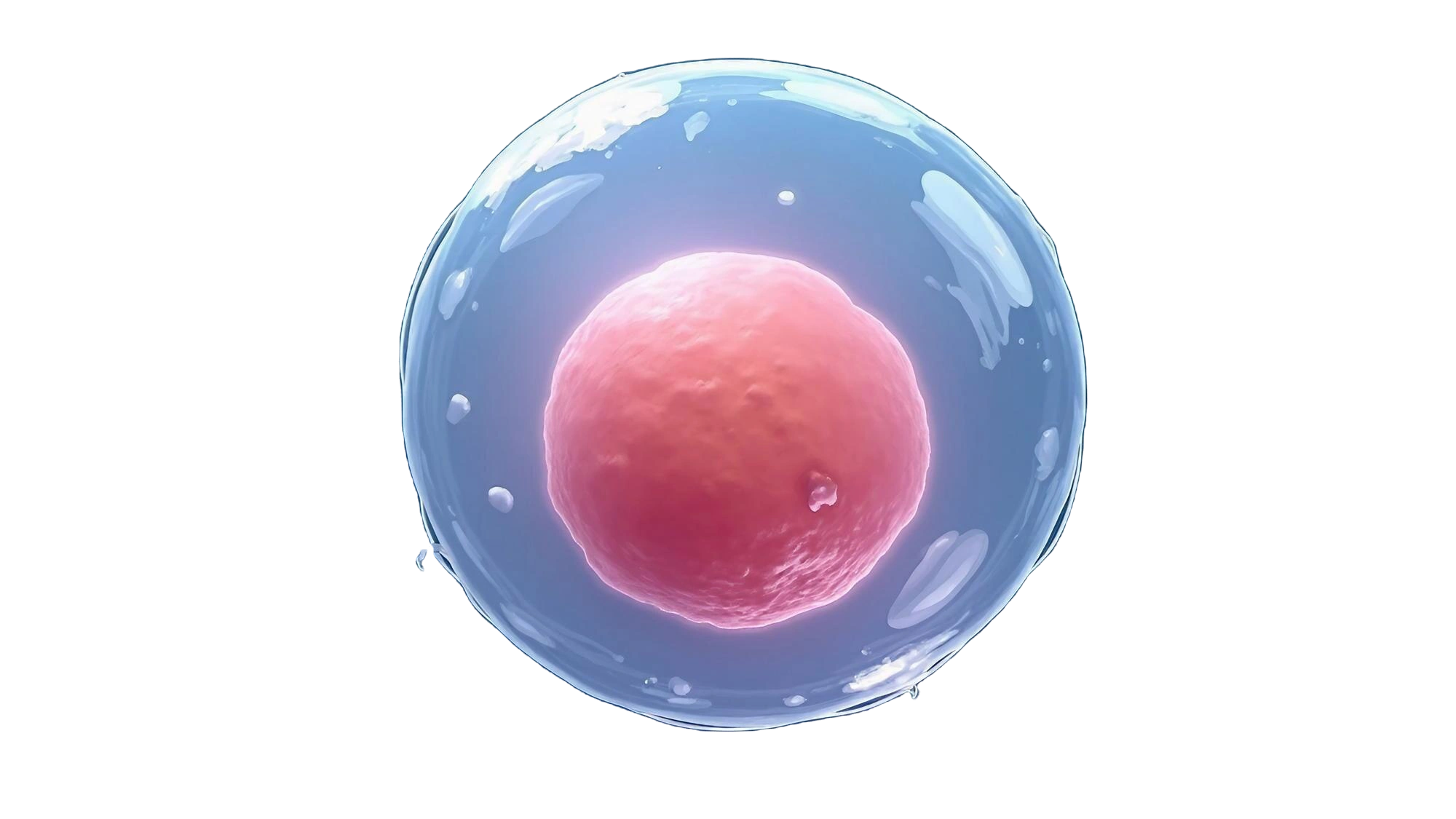
Egg freezing is a method of preserving a woman’s reproductive potential by extracting eggs from her ovaries and freezing them unfertilized for later use. These eggs can be thawed, fertilised with sperm, and implanted in the uterus when the woman is ready to pursue pregnancy.
Unlike embryos, which are eggs fertilised by sperm before freezing, egg freezing offers more autonomy because a partner or sperm donor isn’t required at the time of freezing. Once frozen, eggs can remain viable for many years, and when the woman is ready to conceive, they can be thawed, fertilised, and used in an in-vitro fertilisation (IVF) process.
Who Should Consider Egg Freezing?
There are various reasons why a woman might consider egg freezing, including:
- Delaying Parenthood: Women who wish to pursue higher education, advance their careers, or wait for the right partner can preserve their fertility by freezing their eggs during their most fertile years, typically in their 20s and early 30s.
- Medical Reasons: Women undergoing treatments that could compromise their fertility, such as chemotherapy or radiation for cancer, may opt to freeze their eggs before treatment begins. Women with conditions like endometriosis or ovarian disease, which can affect egg quantity and quality, may also consider this option.
- Diminished Ovarian Reserve: Some women experience a premature decline in the number and quality of their eggs, a condition known as diminished ovarian reserve. Freezing eggs early in such cases can provide a backup plan for future pregnancy.
- Genetic Conditions: Certain genetic conditions, such as BRCA mutations, increase the risk of premature ovarian failure or require preventive surgeries that remove the ovaries. Egg freezing offers women in this situation a way to preserve their fertility.
The Egg Freezing Process
Egg freezing involves several steps, which typically take about two to four weeks:
- Ovarian Stimulation: The first step is stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. This is done with hormone injections over a period of about 10-14 days. Regular monitoring through blood tests and ultrasounds helps doctors track the development of the eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: Once the eggs are mature, they are retrieved in a minor surgical procedure called transvaginal ultrasound aspiration. The patient is sedated, and a needle is used to collect the eggs from the ovaries. This procedure typically takes about 20 minutes, and recovery is usually quick.
- Freezing the Eggs: The collected eggs are then frozen using a process called vitrification, a rapid freezing technique that prevents ice crystals from forming and damaging the egg’s structure. Vitrified eggs can be stored for years, preserving the possibility of future pregnancy.
What to Consider Before Freezing Your Eggs
While egg freezing offers an incredible opportunity for fertility preservation, it’s essential to weigh several key factors before moving forward:
- Age and Success Rates: The success of egg freezing depends largely on the age at which the eggs are frozen. Women under 35 tend to have higher success rates, as eggs from younger women are generally of better quality. After age 37, both the quantity and quality of a woman’s eggs start to decline more rapidly.
- Cost: Egg freezing can be expensive. The cost of one cycle, which includes medications, monitoring, and the retrieval procedure, ranges from $6,000 to $15,000, depending on location and clinic. Multiple cycles may be needed to collect a sufficient number of eggs, and there are also annual storage fees for keeping the eggs frozen.

- Emotional and Physical Considerations: The process involves hormone injections, frequent clinic visits, and a minor surgical procedure, which can be physically and emotionally demanding. Understanding the physical toll and potential side effects is crucial for those considering egg freezing.
- No Guarantee: While egg freezing can extend fertility potential, it does not guarantee a future pregnancy. Not all frozen eggs survive the thawing process, and some may not fertilise or develop into a healthy embryo. Therefore, it’s important to approach egg freezing with realistic expectations.
Conclusion
Egg freezing is a powerful tool that provides women with more reproductive flexibility. Whether you’re focusing on your career, facing a medical challenge, or simply want to keep your options open for the future, egg freezing can offer peace of mind. However, like any medical decision, it requires careful consideration of factors such as age, cost, and potential outcomes. Consulting with a fertility specialist can help you make an informed choice and determine whether egg freezing is the right option for you.
